How To Input meter Data Into computer Software – A Comprehensive Guide!
Inputting meter data requires accurate readings, software configuration, verification, automation, and regular backups to ensure efficiency.
This comprehensive guide will help you how to input meter data into computer software to understand the steps involved in entering meter data into computer software, including best practices and tips for accuracy.
Table of Contents
Choose the Right Software for Meter Data Management:
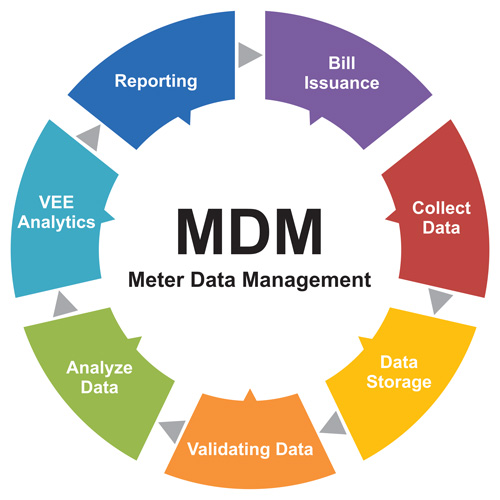
The first step to accurately inputting meter data is selecting the right software. Various software solutions cater to different needs, so you need to choose one that aligns with your organization’s requirements.
Below are some software categories commonly used for meter data management:
Types of Meter Management Software:
- Meter Reading Software: Specifically designed for tracking utility consumption like water, electricity, and gas. These applications are equipped to handle meter reading, billing, and maintenance tracking.
- Energy Management Systems (EMS): Ideal for managing energy usage across a facility or organization. These systems help track energy consumption, detect inefficiencies, and provide insights for sustainability.
- Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) Software: For large-scale organizations, ERP systems like SAP or Oracle often include modules for meter management. These systems help integrate meter data into the company’s broader financial and operational data management framework.
- Automated Meter Reading (AMR) and Smart Metering Systems: These are advanced systems that collect data remotely from digital meters using wireless technology, often integrating seamlessly with the software.
By evaluating your specific needs, you can select the software that best fits your business processes, whether it’s a simple stand-alone tool or a more comprehensive integrated system.
Gather Accurate Meter Data:
Before entering any data into your software, ensure that you have accurate meter readings. Meter data can come from either manual readings or automated systems, depending on the technology your organization uses.
Manual Meter Readings:
If you are using traditional analog meters, you’ll need to record the values displayed on the meter dial. Some key points to keep in mind:
- Accuracy: Double-check the meter reading to avoid errors.
- Units: Ensure you note the correct units of measurement (e.g., kilowatt-hours (kWh) for electricity, gallons or cubic meters for water).
- Time Stamping: Record the exact date and time of the reading, especially if readings are taken at different intervals.
Automated Meter Readings (Smart Meters):
Many modern systems use smart meters that automatically send meter data to your software, saving time and reducing the chances of human error. Here are some benefits of automated readings:
- Remote Data Collection: Data can be pulled without physical visits to the meter location, making the process more efficient.
- Real-time Updates: Automated systems can provide real-time or near-real-time data updates, allowing for better decision-making.
- Reduced Labor Costs: Automated systems reduce the need for manual readings, cutting down on operational costs.
Set Up the Software for Data Entry:
Before inputting any data, it’s essential to prepare the software to ensure you capture the necessary information accurately. This involves configuring the software to match the specifics of your business, such as the type of meters, the measurement units, and the reporting periods.
Key Setup Steps:
- Login: Access the software with your credentials. If you don’t have an account, you may need to create one.
- Create a Project or Data Entry Profile: Most meter management software allows you to create profiles or projects for different locations or meter types. This step helps organize the data efficiently.
- Configure Fields for Data Entry: Customize the input fields to ensure all necessary information is included, such as:
- Meter ID or number
- Location of the meter
- Date and time of the reading
- Consumption data (e.g., kWh, cubic meters, etc.)
- Notes (e.g., any maintenance performed or issues with the meter)
This setup ensures that your entries are aligned with your reporting and analysis needs.
Read More: Is Cisco Fpr Software Or Hardware
Enter the Meter Data into the Software:
Once the software is set up and ready for data entry, it’s time to input the actual meter data. Depending on the software and the type of data collection method you’re using (manual or automated), you will have different ways to input the data.
Manual Data Entry:
If you’re entering data manually, follow these steps:
- Select the Appropriate Meter or Location: Choose the meter you are recording data for, whether it’s a water meter, electricity meter, or gas meter.
- Input the Meter Reading: Enter the reading exactly as recorded. Double-check the units and format.
- Additional Information: Add any relevant information such as the condition of the meter or if a technician performed maintenance.
Automated Data Entry:
If your software is integrated with automated systems (like smart meters or remote data loggers), data may be entered automatically into the system. If this is the case:
- Sync the Data: Ensure that the software is synced with the meter, allowing real-time data transfers.
- Review the Data: Even automated systems may have occasional errors, so it’s important to review the data for discrepancies before finalizing.
Verify the Data for Accuracy:
After entering the data, it’s crucial to verify that everything is correct before saving. Verification ensures that there are no errors or discrepancies that might affect future reports or billing processes.
How to Verify Data:
- Cross-check Meter Readings: Ensure the entered values match what’s displayed on the meter. Compare data with previous entries to spot any outliers.
- Check Time Stamps: Ensure that the time and date match the actual reading period to maintain consistency and reliability.
- Review Calculations: Some systems may automatically calculate consumption (e.g., subtracting previous readings from current ones). Make sure these calculations are correct.
Save and Backup the Data:

Once you’ve verified the data, it’s time to save it in the system. Many software tools allow you to save data manually or automatically at regular intervals. Be sure to follow the best practices for saving and backing up data.
Best Practices for Data Storage:
- Save Regularly: Ensure the software automatically saves the entered data. Set up auto-backups to avoid losing information.
- Create Backups: Regularly back up data to an external drive or cloud storage to prevent loss due to system failures or errors.
- Organize Data Files: Keep your data organized by grouping them by meter type, location, or period for easy access in the future.
Generate Reports and Analyze the Data:
One of the most valuable aspects of inputting meter data into software is the ability to generate reports. After saving the data, you can create detailed reports that offer insights into consumption patterns, operational efficiency, and potential cost savings.
Types of Reports You Can Generate:
- Consumption Reports: See how much energy, water, or gas was consumed over a specified period.
- Billing Reports: Useful for utility companies to generate accurate customer bills.
- Efficiency Reports: Helps organizations identify areas for improvement in energy consumption or resource management.
- Cost Analysis: Analyzes how much resources are costing your business and suggests ways to reduce consumption.
Set Reminders for Future Data Entry:
If your organization regularly collects meter readings, set reminders or automatic schedules within the software to ensure data is input regularly and on time.
How to Set Up Reminders:
- Schedule Readings: Configure the software to send reminders when it’s time to input new data, based on your billing cycle or other regular intervals.
- Automated Alerts: Many systems allow you to set alerts for abnormal readings or when meter data isn’t entered on time, preventing gaps in your data.
Read More: Can Having Other Antivirus Software Cause Pc To Sluggish
Best Practices for Efficient Meter Data Input:
- Consistency: Always input data at the same intervals to maintain consistency across records.
- Accuracy: Double-check entries to minimize human error, especially when working with manual data.
- Use Automation: Whenever possible, use automated meter reading systems to reduce labor and errors.
- Training: Ensure that all staff members involved in the data entry process are properly trained in using the software and understand the importance of accuracy.
FAQ’S:
1. What is meter data management software?
Meter data management software helps businesses track utility consumption, monitor meter readings, and generate reports for accurate billing and analysis.
2. How do I input meter data into the software?
Meter data can be input manually by entering readings or automatically if the software integrates with smart meters or automated systems.
3. What types of meters can be tracked with this software?
The software can manage data from various meters, including water, gas, and electric meters, depending on the system used.
4. How can I ensure accurate meter data entry?
Double-check readings, verify time stamps, and cross-check data for discrepancies to ensure accuracy in meter data input.
5. Can automated systems help with meter data input?
Yes, automated meter reading systems can collect data remotely, reducing manual effort and minimizing human error in data entry.
Conclusion:
Inputting meter data into computer software might seem like a straightforward task, but it requires careful attention to detail, consistency, and the use of the right tools. By following the steps outlined in this guide,how to input meter data into computer software, you can ensure that your meter data is accurately recorded, stored, and analyzed. Properly inputted data enables businesses to improve resource management, generate precise billing, and make informed decisions based on accurate consumption patterns.