Is Tableua Considered A database – Discover Tableau’s Power!
Yes, Tableau visualizes and analyzes data from external databases but does not store data itself.
In this article, we’ll clarify this misconception and help you understand Tableau’s role in data analysis, its capabilities, and how it differs from a database.
Table of Contents
Tableau vs. Database:

Tableau is a data visualization tool that helps users analyze, visualize, and share data insights through interactive charts, graphs, and dashboards.
It connects to various data sources, including databases, and transforms raw data into easily understandable visuals.
A Database is a structured system used to store, manage, and retrieve data efficiently. It organizes data in tables, rows, and columns, enabling operations like storing, updating, and querying data.
Key Differences:
- Functionality: Databases store and manage data, while Tableau visualizes and analyzes data from external sources.
- Data Handling: Databases organize and store data; Tableau pulls data from databases or other sources for visualization.
- Data Processing: Databases handle large-scale storage and processing, while Tableau focuses on transforming data into visual insights, not on storing data.
Why Tableau is Not a Database:
Tableau is a powerful data visualization tool, but it is not a database. It does not function as a storage solution or a data management system. Here’s why Tableau cannot be considered a database:
No Data Storage:
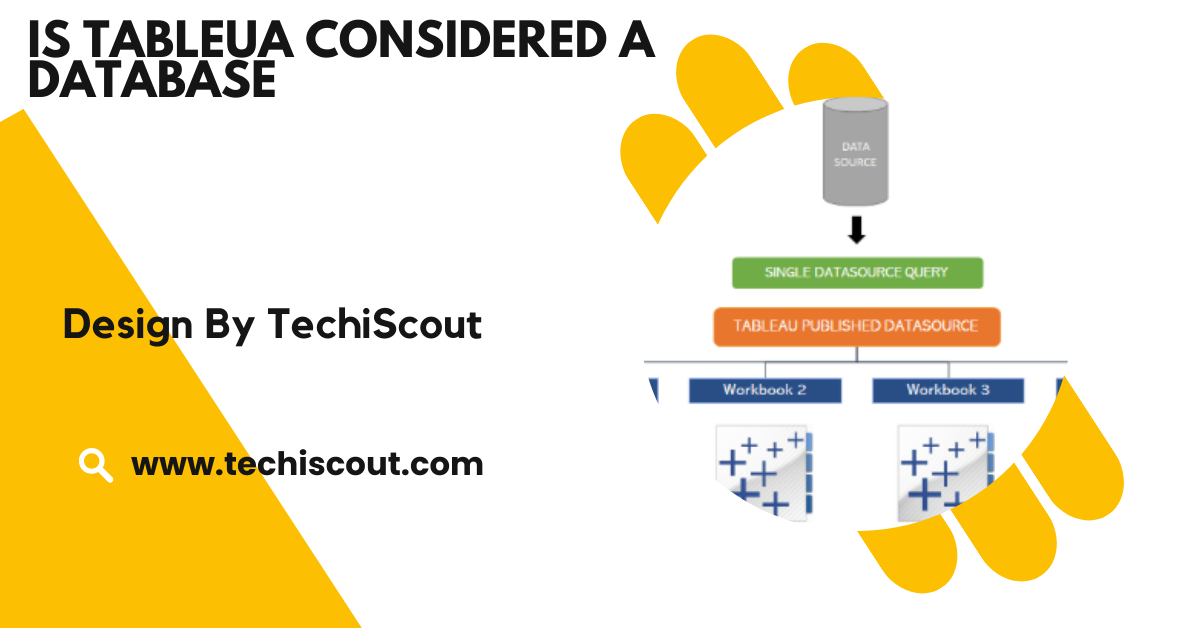
Tableau does not store data. It acts as a bridge between the user and external data sources.
When you connect Tableau to a database (such as MySQL, SQL Server, or Oracle) or other data sources (like Excel or cloud platforms), it retrieves the data from these external systems for analysis and visualization.
The data remains in the original data storage locations, and Tableau simply accesses and visualizes that data. Therefore, if you need a place to store your data for long-term use, a database solution is necessary.
Purpose:
The primary goal of Tableau is not to store or manage data but to help users explore and analyze data through powerful visualizations.
It provides a user-friendly interface for creating interactive charts, graphs, and dashboards that make it easier to understand complex data.
In contrast, databases are specifically designed to handle the storage, retrieval, and manipulation of data in an organized, structured manner. While Tableau plays an essential role in data analysis, it does not perform the core functions of a database, such as indexing, querying, or ensuring data integrity.
Data Connections:
Tableau’s strength lies in its ability to connect to a wide variety of data sources. Whether it’s a traditional relational database like MySQL or SQL Server, or modern cloud-based platforms like Google BigQuery or Amazon Redshift, Tableau can seamlessly pull data from these sources.
Once connected, Tableau transforms this raw data into meaningful visualizations. However, Tableau itself does not replace these databases.
How Tableau Works with Databases:
Tableau is a powerful data visualization tool that integrates with various databases to enable seamless data analysis.
It allows users to connect, import, and visualize data from different sources, including popular relational databases like SQL Server, MySQL, and PostgreSQL, as well as cloud-based solutions like Google BigQuery and Amazon Redshift.
Key Features:
- Live Connections vs. Extracts: Tableau supports live connections for real-time data access and data extracts for faster performance with large datasets.
- Data Blending: Users can combine data from multiple sources for comprehensive analysis.
- Querying and Aggregation: Tableau automatically generates SQL queries to retrieve data and can aggregate, filter, and summarize it.
- Data Transformation: Tableau allows users to clean and reshape data without modifying the original database.
- Data Security: Tableau respects database security settings, ensuring proper data governance.
- Visualization and Analysis: Users can create interactive charts and dashboards with Tableau’s drag-and-drop interface.
- Real-Time Collaboration: With Tableau Cloud, teams can collaborate on visualizations in real-time, enabling quicker decision-making.
Read More: How to Become a Software Engineer
Tableau’s Role in Data Analytics:
Tableau is a powerful data visualization tool that plays a crucial role in the data analytics process by providing a means to interpret and analyze data stored in databases.
While it is not a database itself, Tableau enhances the value of data by enabling users to transform raw, complex data into clear, interactive visualizations such as graphs, charts, and dashboards.
Once data is stored in a database, Tableau connects to these sources and helps organizations extract insights by presenting the data in an easily digestible format. This is especially useful for business intelligence (BI) purposes, as it allows companies to make informed, data-driven decisions.
Tableau can handle complex queries and perform aggregations, filtering, and even basic data transformations.
However, it does not replace databases, as its core function is not to store data but to bring data to life through visual storytelling.
It complements databases by providing the means to visualize and analyze data stored within them, making it easier for users regardless of technical expertise—to explore, interpret, and make decisions based on data.
By offering real-time data analysis and seamless integration with various databases, Tableau helps organizations unlock the full potential of their data, making it an essential tool in modern data analytics and business decision-making processes.
FAQ’s:
1.What is Tableau?
Tableau is a data visualization tool that allows users to analyze and create interactive visualizations from various data sources.
2.Can Tableau store data?
No, Tableau does not store data. It connects to external data sources to visualize and analyze it.
3.What is the primary function of a database?
A database is used to store, manage, and retrieve large volumes of structured data efficiently.
4.How does Tableau work with databases?
Tableau connects to databases and pulls data from them to create visualizations, but it does not replace the database.
5.Is Tableau a substitute for a database?
No, Tableau is a complementary tool for visualizing data, not a substitute for a database, which is used for storing and managing data.
Conclusion
To sum up, Tableau is not a database. It is a powerful visualization tool that connects to various data sources, including databases, to provide insights through interactive charts, graphs, and dashboards. While databases are used to store and manage data, Tableau is used to analyze and present that data in a visually compelling way.Tableau is an excellent choice for transforming that data into actionable insights.
Related Articles:
- Read More: iCUE Software
- Read More: What Is The Suggested First Step For Entering Software Development
- Read More: How Useful is Master in Software Engineering